Dr.
Gerald S. Hecht
Associate
Professor of Psychology
College
of Sciences
webmaster@psiwebsubr.org
PSYC 210 - General Psychology Exam 3 Study
Guide
- THE BRAIN MECHANISMS OF LEARNING
Midbrain: "reinforcement circuits"
The Nucleus Accumbens (NA) and Ventral Tegmental (VTA) circuit.
Millions of axons project from cell bodies in the VTA to the NA where they release
dopamine as a neurotransmitter. The VTA in turn sends axons back to the NA where they release
GABA as their neurotransmitter.
The dendrites of the neurons in the VTA have receptors for the following neurotransmitters:
nicotinic ACh
B-endorphin
Anandamide
GABA
Every known type of
recreational drug (drugs that are taken deliberately by people for no
medical reason) acts biochemically somewhere in the VTA-NA brain
circuit:
cocaine & amphetamines = dopamine
alcohol, Valium, Xanax, Rohypnol, etc = GABA
Heroin, morphine, codeine, Dilaudid, Demerol, Vicodin, etc = B-endorphin
Cigarettes, Cigars, chewing tobacco, etc = nicotinic ACh
Marijuana, hashish, etc = Anandamide
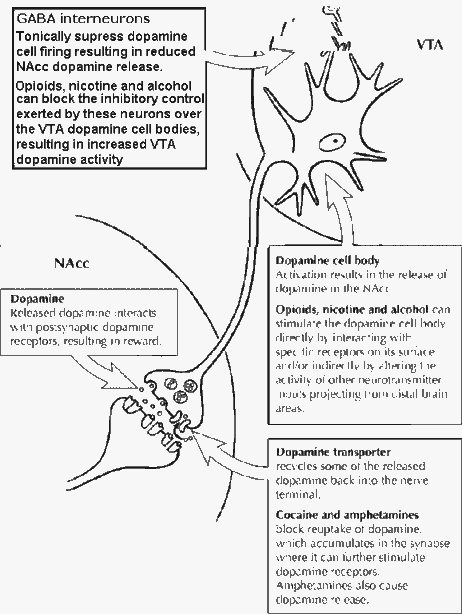
- The VTA-NA plays a vital role in the psychological phenomenon known as OPERANT LEARNING.
DEFINITIONS:
OPERANT LEARNING– Behavior is a function of its consequences
Positive Reinforcement:
strengthens learning by giving the subject something that increases its behavior (usually something desirable)
Negative Reinforcement:
strengthens learning by removing something painful or aversive (note: also increases behavior)
Positive Punishment:
weakens learning by giving the subject something that decreases its behavior (usually something painful)
Negative Punishment:
weakens learning by taking away something that the subject finds reinforcing… (note: also decreases behavior).
- BE PREPARED TO ANSWER QUESTIONS ABOUT THORNDIKE’S DISCRETE TRIALS
OPERANT STUDIES AND SKINNER’S FREE RUNNING OPERANT STUDIES (SCHEDULES
OF REINFORCEMENT, ETC)
- KNOW THE PATTERNS OF RESPONDING THAT ARE TYPICAL OF FIXED RATIO (FR) AND FIXED INTERVAL (FI) SCHEDULES OF REINFORCEMENT
- REINFORCEMENT "WORKS" BY INCREASING ACTIVITY IN THE VTA-NA
CIRCUIT! THUS RECREATIONAL DRUG USE IS A TYPE OF LEARNING--THE BEHAVIOR
THAT IS REINFORCED BY THE DRUG IS THAT OF OBTAINING AND ADMINISTERING
THE DRUG!
- CLASSICAL (PAVLOVIAN) LEARNING
DEFINITIONS:
A neutral stimulus occurs with a stimulusthat evokes a reflex;
eventually, the neutral stimulus comes to evoke a response which is
almost identical to the reflex.
Conditioned = learned
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
Conditioned Response (CR)
Unconditioned = a "hardwired" reflex which does not have to be learned.
Unconditioned Stimulus (US)
Unconditioned Response (UR)
Neutral = not involved in the unlearned reflex at all.
Neutral Stimulus (NS)
Orienting Reflex (OR)
Pavlov's "Classic" research with dogs
US(meat powder) leads to UR(salivation)NS (bell) leads to OR (dog attends to bell)
NS (bell) + US (meat) leads to UR (salivation to meat and bell).
CS (bell) leads to CR (salivation to bell alone).
Secondary Reinforcers (e.g., Money):
evidence of Pavlovian elements in Operant Learning.


